| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2012-10-24 09:54:58 -0600 |
|---|
| Update Date | 2015-12-09 12:06:48 -0700 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
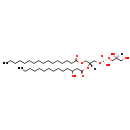
| Name: | PG(14:0(3-OH)/16:0) |
|---|
| Description | PG(14:0(3-OH)/16:0) is a phosphatidylglycerol. Phosphatidylglycerols consist of a glycerol 3-phosphate backbone esterified to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached to the C-1 and C-2 positions. PG(14:0(3-OH)/16:0), in particular, consists of one 3-hydroxytetradecanoyl chain to the C-1 atom, and one hexadecanoyl to the C-2 atom. In E. coli glycerophospholipid metabolism, phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate) by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via two intermediates, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol) and phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP, a phosphorylated phosphatidylglycerol). Phosphatidylglycerols, along with CDP-diacylglycerol, also serve as precursor molecules for the synthesis of cardiolipin, a phospholipid found in membranes. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 1-3-hydroxytetradecanoyl-2-hexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1'-glycerol)
- 1-3-hydroxytetradecanoyl-2-hexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol
- 1-3-hydroxytetradecanoyl-2-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol
- GPG(14:0/16:0)
- GPG(30:0)
- PG(14:0/16:0)
- PG(30:0)
- Phosphatidylglycerol(14:0/16:0)
- Phosphatidylglycerol(30:0)
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula: | C36H71O11P |
|---|
| Weight: | Average: 710.927
Monoisotopic: 710.473400104 |
|---|
| InChI Key: | IHKIIANQOPGRTI-PRIWKQAOSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C36H71O11P/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-14-15-16-18-20-22-24-26-35(40)44-30-34(31-46-48(42,43)45-29-33(39)28-37)47-36(41)27-32(38)25-23-21-19-17-12-10-8-6-4-2/h32-34,37-39H,3-31H2,1-2H3,(H,42,43)/t32?,33-,34+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| CAS number: | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | [(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy][(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)oxy]propoxy]phosphinic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | (2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropoxy((2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(3-hydroxytetradecanoyl)oxy]propoxy)phosphinic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | [H][C@](O)(CO)COP(O)(=O)OC[C@@]([H])(COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CC(O)CCCCCCCCCCC |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phosphatidylglycerols. These are glycerophosphoglycerols in which two fatty acids are bonded to the 1-glycerol moiety through ester linkages. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Glycerophospholipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycerophosphoglycerols |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phosphatidylglycerols |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 1,2-diacylglycerophosphoglycerol
- Beta-hydroxy acid
- Dialkyl phosphate
- Fatty acid ester
- Fatty acyl
- Alkyl phosphate
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Hydroxy acid
- 1,2-diol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Primary alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxide
- Alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: | Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -1 |
|---|
| Melting point: | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: | |
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: | Membrane |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways: | | phospholipid biosynthesis (CL(16:0/14:0(3-OH)/16:0/14:0(3-OH))) | PW001951 |    |
|
|---|
| KEGG Pathways: | - Glycerophospholipid metabolism ec00564
|
|---|
| EcoCyc Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: | |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Yuan Y, Leeds JA, Meredith TC (2012). "Pseudomonas aeruginosa Directly Shunts β-Oxidation Degradation Intermediates into De Novo Fatty Acid Biosynthesis." J Bacteriol. 194(19):5185-96 Pubmed: 22753057
- Yurtsever D. (2007). Fatty acid methyl ester profiling of Enterococcus and Esherichia coli for microbial source tracking. M.sc. Thesis. Villanova University: U.S.A
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| Links |
|---|
| External Links: | | Resource | Link |
|---|
| CHEBI ID | Not Available | | HMDB ID | Not Available | | Pubchem Compound ID | Not Available | | Kegg ID | Not Available | | ChemSpider ID | Not Available | | Wikipedia ID | Not Available | | BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|
|---|