| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2012-08-09 09:25:15 -0600 |
|---|
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 17:21:42 -0600 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Name: | D-Tyrosine |
|---|
| Description | D-Tyrosine is one of the two enantiomers of tyrosine. Tyrosine (abbreviated as Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, is one of the 22 amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. Its codons are UAC and UAU. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. (Wikipedia) L-Tyrosine is the correct tyrosine isomer used in building proteins, and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases ensure the exclusion of D-amino acids like D-tyrosine from translation. But sometimes, tyrosyl-tRNA synthetases use D-tyrosine by mistake. Hence, D-tyrosine can be toxic to E. coli, especially in absence of D-Tyr-tRNATyr deacylase to remove the incorrectly-made tRNAs containing D-tyrosine. (PMID 15292242) |
|---|
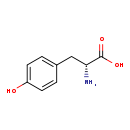
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms: | - (-)-a-Amino-p-hydroxyhydrocinnamate
- (-)-a-Amino-p-hydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
- (-)-alpha-Amino-p-hydroxyhydrocinnamate
- (-)-alpha-Amino-p-hydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
- (-)-α-amino-P-Hydroxyhydrocinnamate
- (-)-α-amino-P-Hydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
- (2R)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
- (2R)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- (R)-2-Amino-3-(p-hydroxyphenyl)propionate
- (R)-2-Amino-3-(p-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid
- (R)-3-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)alanine
- (S)-(-)-Tyrosine
- (S)-2-Amino-3-(p-hydroxyphenyl)propionate
- (S)-2-amino-3-(p-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid
- (S)-3-(p-hydroxyphenyl)alanine
- (S)-a-amino-4-hydroxy-Benzenepropanoate
- (S)-a-amino-4-hydroxy-Benzenepropanoic acid
- (S)-a-Amino-4-hydroxybenzenepropanoate
- (S)-a-Amino-4-hydroxybenzenepropanoic acid
- (S)-alpha-amino-4-hydroxy-Benzenepropanoate
- (S)-alpha-amino-4-hydroxy-Benzenepropanoic acid
- (S)-alpha-Amino-4-hydroxybenzenepropanoate
- (S)-alpha-Amino-4-hydroxybenzenepropanoic acid
- (S)-Tyrosine
- (S)-α-amino-4-Hydroxy-benzenepropanoate
- (S)-α-amino-4-Hydroxy-benzenepropanoic acid
- (S)-α-amino-4-Hydroxybenzenepropanoate
- (S)-α-amino-4-Hydroxybenzenepropanoic acid
- 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphen yl)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-Propanoate
- 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphen yl)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-Propanoic acid
- 2-amino-3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-propanoate
- 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-propanoic acid
- 3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine
- 4-Hydroxy-L-Phenylalanine
- Benzenepropanoate
- Benzenepropanoic acid
- D-Tyr
- D-Tyrosin
- D-Tyrosine
- L-p-Tyrosine
- L-Tyrosine
- P-Tyrosine
- Tyr
- Tyrosine
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula: | C9H11NO3 |
|---|
| Weight: | Average: 181.1885
Monoisotopic: 181.073893223 |
|---|
| InChI Key: | OUYCCCASQSFEME-MRVPVSSYSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C9H11NO3/c10-8(9(12)13)5-6-1-3-7(11)4-2-6/h1-4,8,11H,5,10H2,(H,12,13)/t8-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| CAS number: | 556-02-5 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | (2R)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | (.+-.)-tyrosine |
|---|
| SMILES: | N[C@H](CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tyrosine and derivatives. Tyrosine and derivatives are compounds containing tyrosine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of tyrosine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tyrosine and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tyrosine or derivatives
- Phenylalanine or derivatives
- 3-phenylpropanoic-acid
- Alpha-amino acid
- Amphetamine or derivatives
- D-alpha-amino acid
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Phenol
- Aralkylamine
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: | Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | 0 |
|---|
| Melting point: | 343 °C |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: | | Property | Value | Source |
|---|
| Water Solubility: | 0.453 mg/mL at 25 deg C; 0.479 mg/mL | PhysProp | | LogP: | -2.26 [HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995)] | PhysProp |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| EcoCyc Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: | |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - Soutourina, O., Soutourina, J., Blanquet, S., Plateau, P. (2004). "Formation of D-tyrosyl-tRNATyr accounts for the toxicity of D-tyrosine toward Escherichia coli." J Biol Chem 279:42560-42565. Pubmed: 15292242
- Winder, C. L., Dunn, W. B., Schuler, S., Broadhurst, D., Jarvis, R., Stephens, G. M., Goodacre, R. (2008). "Global metabolic profiling of Escherichia coli cultures: an evaluation of methods for quenching and extraction of intracellular metabolites." Anal Chem 80:2939-2948. Pubmed: 18331064
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| Links |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|