Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate (M2MDB001024)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 14:31:35 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 17:19:28 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | N-acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate is a member of the chemical class known as Sugar Acids and Derivatives. These are compounds containing a saccharide unit which bears a carboxylic acid group. The enzyme MurQ is an N-acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate (MurNAc 6-phosphate) hydrolase (or etherase) that hydrolyzes the lactyl side chain from MurNAc 6-phosphate and generates GlcNAc 6-phosphate. (PMID 18837509). It is a key component of peptidoglycan synthesis. The peptidoglycan synthesis pathway starts at the cytoplasm, where in six steps the peptidoglycan precursor a UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide is synthesized. This precursor is then attached to the memberane acceptor all-trans-undecaprenyl phosphate, generating a N-acetylmuramoyl-pentapeptide-diphosphoundecaprenol, also known as lipid I. Another transferase then adds UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine, yielding the complete monomeric unit a lipid , also known as lipid . This final lipid intermediate is transferred through the membrane. The peptidoglycan monomers are then polymerized on the outside surface by glycosyltransferases, which form the linear glycan chains, and transpeptidases, which catalyze the formation of peptide crosslinks. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
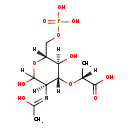
| Chemical Formula: | C11H20NO11P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 373.2504 Monoisotopic: 373.077396999 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | NMEMTQKUEVNSPV-MKFCKLDKSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C11H20NO11P/c1-4(10(15)16)22-9-7(12-5(2)13)11(17)23-6(8(9)14)3-21-24(18,19)20/h4,6-9,11,14,17H,3H2,1-2H3,(H,12,13)(H,15,16)(H2,18,19,20)/t4-,6-,7-,8-,9-,11?/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2R)-2-{[(3R,4R,5S,6R)-2,5-dihydroxy-3-[(1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-6-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxan-4-yl]oxy}propanoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | MurNAc 6-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [H][C@](C)(O[C@@]1([H])[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]([H])(COP(O)(O)=O)OC([H])(O)[C@]1([H])N=C(C)O)C(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Acylaminosugars | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Phosphoenolpyruvic acid + N-Acetyl-D-muramoate > N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate + Pyruvic acid 1,6-Anhydro-N-acetylmuramate + Adenosine triphosphate + Water > N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate + ADP + Hydrogen ion N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate + Water <> N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine 6-Phosphate + D-Lactic acid N-Acetyl-D-muramoate + Protein N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine <> N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate + Protein histidine Phosphoenolpyruvic acid + <i>N</i>-acetylmuramate > N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate + Pyruvic acid Adenosine triphosphate + 1,6-Anhydro-N-acetyl-beta-muramate + Water > ADP + N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate + Water > N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine 6-Phosphate + D-Lactic acid Adenosine triphosphate + 1,6-Anhydro-N-acetyl-beta-muramate + Water <> ADP + N-Acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- General (non sugar-specific) component of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS). This major carbohydrate active-transport system catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. Enzyme I transfers the phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to the phosphoryl carrier protein (HPr)
- Gene Name:
- ptsI
- Uniprot ID:
- P08839
- Molecular weight:
- 63561
Reactions
| Phosphoenolpyruvate + protein L-histidine = pyruvate + protein N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in sugar:hydrogen symporter activity
- Specific function:
- The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS), a major carbohydrate active -transport system, catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. This system is involved in glucose transport
- Gene Name:
- crr
- Uniprot ID:
- P69783
- Molecular weight:
- 18251
Reactions
| Protein EIIA N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine + protein EIIB = protein EIIA + protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in carbon-oxygen lyase activity
- Specific function:
- Specifically catalyzes the cleavage of the D-lactyl ether substituent of MurNAc 6-phosphate, producing GlcNAc 6- phosphate and D-lactate. Is required for growth on MurNAc as the sole source of carbon and energy. Together with AnmK, is also required for the utilization of anhydro-N-acetylmuramic acid (anhMurNAc) either imported from the medium or derived from its own cell wall murein, and thus plays a role in cell wall recycling
- Gene Name:
- murQ
- Uniprot ID:
- P76535
- Molecular weight:
- 31220
Reactions
| N-acetylmuramate 6-phosphate + H(2)O = N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate + D-lactate. |
- General function:
- Involved in protein-N(PI)-phosphohistidine-sugar phosphotransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS), a major carbohydrate active -transport system, catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. This system is involved in N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) transport, yielding cytoplasmic MurNAc-6-P. Is responsible for growth on MurNAc as the sole source of carbon and energy. Is also able to take up anhydro-N-acetylmuramic acid (anhMurNAc), but cannot phosphorylate the carbon 6, probably because of the 1,6- anhydro ring
- Gene Name:
- murP
- Uniprot ID:
- P77272
- Molecular weight:
- 49801
Reactions
| Protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine + sugar = protein EIIB + sugar phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in ATP binding
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of 1,6-anhydro-N- acetylmuramic acid (anhMurNAc) with the simultaneous cleavage of the 1,6-anhydro ring, generating MurNAc-6-P. Is required for the utilization of anhMurNAc either imported from the medium or derived from its own cell wall murein, and thus plays a role in cell wall recycling
- Gene Name:
- anmK
- Uniprot ID:
- P77570
- Molecular weight:
- 39496
Reactions
| ATP + 1,6-anhydro-N-acetyl-beta-muramate + H(2)O = ADP + N-acetylmuramate 6-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in sugar:hydrogen symporter activity
- Specific function:
- General (non sugar-specific) component of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS). This major carbohydrate active-transport system catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. The phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is transferred to the phosphoryl carrier protein HPr by enzyme I. Phospho-HPr then transfers it to the permease (enzymes II/III)
- Gene Name:
- ptsH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA04
- Molecular weight:
- 9119
Reactions
| Protein HPr N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine + protein EIIA = protein HPr + protein EIIA N(tau)-phospho-L-histidine. |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in protein-N(PI)-phosphohistidine-sugar phosphotransferase activity
- Specific function:
- The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS), a major carbohydrate active -transport system, catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. This system is involved in N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) transport, yielding cytoplasmic MurNAc-6-P. Is responsible for growth on MurNAc as the sole source of carbon and energy. Is also able to take up anhydro-N-acetylmuramic acid (anhMurNAc), but cannot phosphorylate the carbon 6, probably because of the 1,6- anhydro ring
- Gene Name:
- murP
- Uniprot ID:
- P77272
- Molecular weight:
- 49801
Reactions
| Protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine + sugar = protein EIIB + sugar phosphate. |