| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 14:25:54 -0600 |
|---|
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 17:19:15 -0600 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
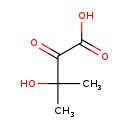
| Name: | 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid |
|---|
| Description | 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid belongs to the class of Branched Fatty Acids. These are fatty acids containing a branched chain. (inferred from compound structure)α-Acetolactic acid (α-acetolactate) is a precursor in the biosynthesis of the branched chain amino acids valine and leucine. α-Acetolactic acid is produced from two molecules of pyruvic acid by acetolactate synthase. α-Acetolactic acid can also be decarboxylated by alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase to produce acetoin. (WikiPedia) |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms: | - 2-Oxo-3-hydroxyisovalerate
- 2-Oxo-3-hydroxyisovaleric acid
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxo-butanoate
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxo-butanoic acid
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula: | C5H8O4 |
|---|
| Weight: | Average: 132.1146
Monoisotopic: 132.042258744 |
|---|
| InChI Key: | DNOPJXBPONYBLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C5H8O4/c1-5(2,9)3(6)4(7)8/h9H,1-2H3,(H,7,8) |
|---|
| CAS number: | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | 2-oxo-3-hydroxyisovaleric acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | CC(C)(O)C(=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as short-chain keto acids and derivatives. These are keto acids with an alkyl chain the contains less than 6 carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Short-chain keto acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Branched fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Short-chain keto acid
- Methyl-branched fatty acid
- Alpha-keto acid
- Acyloin
- Fatty acyl
- Tertiary alcohol
- Alpha-hydroxy ketone
- Ketone
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: | Not Available |
|---|
| Charge: | -1 |
|---|
| Melting point: | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: | |
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways: | | Secondary Metabolites: Valine and I-leucine biosynthesis from pyruvate | PW000978 |    |
|
|---|
| KEGG Pathways: | - Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis ec00290
|
|---|
| EcoCyc Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: | |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Yurtsever D. (2007). Fatty acid methyl ester profiling of Enterococcus and Esherichia coli for microbial source tracking. M.sc. Thesis. Villanova University: U.S.A
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| Links |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|