Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Betaine (M2MDB000564)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 14:02:31 -0600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-10-15 16:14:21 -0600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Betaine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Betaine or trimethylglycine is a methylated derivative of glycine. It functions as a methyl donor in that it carries and donates methyl functional groups to facilitate necessary chemical processes. Betaine is an osmoprotectant compound. The accumulation of betaine increases the volume of cytoplasmic water of E. coli and increases the growth rate of osmotically stressed E. coli. (PMID: 1537801) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
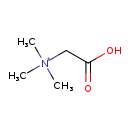
| Chemical Formula: | C5H12NO2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 118.1543 Monoisotopic: 118.086803633 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C5H11NO2/c1-6(2,3)4-5(7)8/h4H2,1-3H3/p+1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 107-43-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (carboxymethyl)trimethylazanium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | trimethyl glycine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | C[N+](C)(C)CC(O)=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 293 °C ( Soicke, H., Fitoterapia 1988, V59(1), P73-5); 301 oC dec. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Adenosine triphosphate + Water + Betaine > ADP + Betaine + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate Adenosine triphosphate + Water + Betaine > ADP + Betaine + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate Betaine aldehyde + Water + NADP > Betaine +2 Hydrogen ion + NADPH Betaine aldehyde + Water + NAD <> Betaine +2 Hydrogen ion + NADH Betaine aldehyde + NADP + Water <> Betaine + NADPH +2 Hydrogen ion Betaine aldehyde + NAD + Water > Hydrogen ion + Betaine + NADH Betaine aldehyde + NAD + Water > Betaine + NADH Betaine aldehyde + Water + NADP > Betaine +2 Hydrogen ion + NADPH Betaine aldehyde + Water + NADP > Betaine +2 Hydrogen ion + NADPH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Mu, Yun; Guo, Xiao-hui. Improved process for preparation of betaine. Huaxue Yu Shengwu Gongcheng (2005), 22(7), 48-49. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Betaine aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = betaine + NADH
- Gene Name:
- betB
- Uniprot ID:
- P17445
- Molecular weight:
- 52911
Reactions
| Betaine aldehyde + NAD(+) + H(2)O = betaine + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proW
- Uniprot ID:
- P14176
- Molecular weight:
- 37619
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehW
- Uniprot ID:
- P33359
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehY
- Uniprot ID:
- P33361
- Molecular weight:
- 41138
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yehX
- Uniprot ID:
- P33360
- Molecular weight:
- 34424
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules
- Gene Name:
- osmF
- Uniprot ID:
- P33362
- Molecular weight:
- 32609
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable transporter whose substrate is unknown. Is not involved in aerobic D-malate transport
- Gene Name:
- yeaV
- Uniprot ID:
- P0ABD1
- Molecular weight:
- 52881
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Proton symporter that senses osmotic shifts and responds by importing osmolytes such as proline, glycine betaine, stachydrine, pipecolic acid, ectoine and taurine. It is both an osmosensor and an osmoregulator which is available to participate early in the bacterial osmoregulatory response
- Gene Name:
- proP
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C0L7
- Molecular weight:
- 54845
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a multicomponent binding-protein-dependent transport system for glycine betaine/L-proline
- Gene Name:
- proW
- Uniprot ID:
- P14176
- Molecular weight:
- 37619
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehW
- Uniprot ID:
- P33359
- Molecular weight:
- 25514
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- yehY
- Uniprot ID:
- P33361
- Molecular weight:
- 41138
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Non-specific porin
- Gene Name:
- ompN
- Uniprot ID:
- P77747
- Molecular weight:
- 41220
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- yehX
- Uniprot ID:
- P33360
- Molecular weight:
- 34424
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of inorganic phosphate, phosphorylated compounds, and some other negatively charged solutes
- Gene Name:
- phoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P02932
- Molecular weight:
- 38922
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- OmpF is a porin that forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane. It is also a receptor for the bacteriophage T2
- Gene Name:
- ompF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02931
- Molecular weight:
- 39333
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- May be part of an ABC transporter complex involved in uptake of osmoprotectant molecules
- Gene Name:
- osmF
- Uniprot ID:
- P33362
- Molecular weight:
- 32609
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- ompC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06996
- Molecular weight:
- 40368