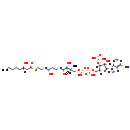| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 14:00:58 -0600 |
|---|
| Update Date | 2015-09-17 15:41:18 -0600 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Name: | (S)-Hydroxyoctanoyl-CoA |
|---|
| Description | Coenzyme A is notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. Since coenzyme A is chemically a thiol, it can react with carboxylic acids to form thioesters, thus functioning as an acyl group carrier. Specifically (S)-Hydroxyoctanoyl-CoA is involved in fatty acid metabolism. It is the product of a reaction between 3-Oxooctanoyl-CoA and two enzymes; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA Dehydrogenase and long-chain- 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms: | - (S)-3-Hydroxyoctanoyl-CoA
- (S)-3-Hydroxyoctanoyl-Coenzyme A
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula: | C29H50N7O18P3S |
|---|
| Weight: | Average: 909.73
Monoisotopic: 909.214588057 |
|---|
| InChI Key: | ATVGTMKWKDUCMS-FZQVHTIWSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C29H50N7O18P3S/c1-4-5-6-7-17(37)12-20(39)58-11-10-31-19(38)8-9-32-27(42)24(41)29(2,3)14-51-57(48,49)54-56(46,47)50-13-18-23(53-55(43,44)45)22(40)28(52-18)36-16-35-21-25(30)33-15-34-26(21)36/h15-18,22-24,28,37,40-41H,4-14H2,1-3H3,(H,31,38)(H,32,42)(H,46,47)(H,48,49)(H2,30,33,34)(H2,43,44,45)/t17-,18+,22?,23-,24-,28+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| CAS number: | 79171-48-5 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | (2R)-4-({[({[(2R,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxy-N-{2-[(2-{[(3S)-3-hydroxyoctanoyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl]ethyl}-3,3-dimethylbutanimidic acid |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | (2R)-4-[({[(2R,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl)oxy]-2-hydroxy-N-{2-[(2-{[(3S)-3-hydroxyoctanoyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)-C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl]ethyl}-3,3-dimethylbutanimidic acid |
|---|
| SMILES: | [H][C@](O)(CCCCC)CC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)[C@]([H])(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H](C(O)[C@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 3-hydroxyacyl coas. These are organic compounds containing a 3-hydroxyl acylated coenzyme A derivative. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl thioesters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 3-hydroxyacyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- N-glycosyl compound
- Glycosyl compound
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- 6-aminopurine
- Purine
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Aminopyrimidine
- Imidolactam
- Alkyl phosphate
- Pyrimidine
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- N-substituted imidazole
- Monosaccharide
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Imidazole
- Azole
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Sulfenyl compound
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboximidic acid derivative
- Carboximidic acid
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Alcohol
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: | Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -3 |
|---|
| Melting point: | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: | |
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways: | |
|---|
| KEGG Pathways: | |
|---|
| EcoCyc Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: | |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | - Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M. (2012). "KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets." Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109-D114. Pubmed: 22080510
- Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Santos-Zavaleta, A., Peralta-Gil, M., Gama-Castro, S., Muniz-Rascado, L., Bonavides-Martinez, C., Paley, S., Krummenacker, M., Altman, T., Kaipa, P., Spaulding, A., Pacheco, J., Latendresse, M., Fulcher, C., Sarker, M., Shearer, A. G., Mackie, A., Paulsen, I., Gunsalus, R. P., Karp, P. D. (2011). "EcoCyc: a comprehensive database of Escherichia coli biology." Nucleic Acids Res 39:D583-D590. Pubmed: 21097882
|
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| Links |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|