| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2012-10-10 12:23:20 -0600 |
|---|
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 17:26:14 -0600 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
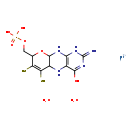
| Name: | molybdenum cofactor |
|---|
| Description | Molybdenum cofactor is a cofactor required for the activity of enzymes such as sulfite oxidase, xanthine oxidoreductase, and aldehyde oxidase. It is a coordination complex formed between molybdopterin (which, despite the name, does not contain molybdenum) and an oxide of molybdenum. Molybdenum-containing enzymes catalyze basic metabolic reactions in the nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon cycles. With the exception of the nitrogenase cofactor, molybdenum is incorporated into proteins as the molybdenum cofactor that contains a mononuclear molybdenum atom coordinated to the sulfur atoms of a pterin derivative named molybdopterin. Certain microorganisms can also utilize tungsten in a similar fashion. Molybdenum-cofactor-containing enzymes catalyze the transfer of an oxygen atom, ultimately derived from or incorporated into water, to or from a substrate in a two-electron redox reaction. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms: | - MCD
- MoCo
- Molybdenum enzyme molybdenum cofactor
- Molybdoenzyme molybdenum-containing cofactor
- Molybdopterin cytosine dinucleotide
- MoO2(OH)DTPP-mCDP
- MoO2(OH)Dtpp-mCDP
- Nitrate reductase molybdenum cofactor
- Nitric acid reductase molybdenum cofactor
- Pterin molybdenum cofactor
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula: | C10H18MoN5O8PS2 |
|---|
| Weight: | Average: 527.32
Monoisotopic: 528.938848315 |
|---|
| InChI Key: | VUKICSJFFDCESC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C10H14N5O6PS2.Mo.2H2O/c11-10-14-7-4(8(16)15-10)12-3-6(24)5(23)2(21-9(3)13-7)1-20-22(17,18)19;;;/h2-3,9,12,23-24H,1H2,(H2,17,18,19)(H4,11,13,14,15,16);;2*1H2/q;+2;; |
|---|
| CAS number: | 73508-07-3 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | molybdenum(2+) ion ({4-hydroxy-2-imino-6,7-disulfanyl-1H,2H,5H,5aH,8H,9aH,10H-pyrano[3,2-g]pteridin-8-yl}methoxy)phosphonic acid dihydrate |
|---|
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | molybdenum(2+) ion molybdopterin cofactor dihydrate |
|---|
| SMILES: | O.O.[Mo++].OC1=NC(=N)NC2=C1NC1C(N2)OC(COP(O)(O)=O)C(S)=C1S |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyranopterins and derivatives. These are pterin derivatives in which a pyran ring is fused either to the pyrimidine ring or the pyrazine ring of the pterin moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Pteridines and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Pterins and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Pyranopterins and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Pyranopterin
- Hydroxypyrimidine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Secondary aliphatic/aromatic amine
- Alkyl phosphate
- Pyrimidine
- Pyran
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organic transition metal salt
- Thioenol
- Secondary amine
- Alkylthiol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic salt
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Organic cation
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State: | Solid |
|---|
| Charge: | -2 |
|---|
| Melting point: | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties: | |
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm |
|---|
| Reactions: | |
|---|
| SMPDB Pathways: | |
|---|
| KEGG Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| EcoCyc Pathways: | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra: | |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| References: | Not Available |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| Links |
|---|
| External Links: | |
|---|