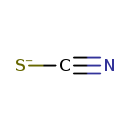Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Thiocyanate (M2MDB001695)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-07-30 14:55:14 -0600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-09-17 15:41:11 -0600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Thiocyanate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Thiocyanate is analogous to the cyanate ion, [OCN]-, wherein oxygen is replaced by sulfur. [SCN]- is one of the pseudohalogens, due to the similarity of its reactions to that of halide ions. Thiocyanate was formerly known as rhodanide (from a Greek word for rose) because of the red color of its complexes with iron. Thiocyanates are typically colorless. Cyanide ions can react with cystine to yield thicocyanate. This reaction occurs to a slight extent even in neutral solution, but is more pronounced in alkaline solutions of cystine. In addition to this non-enzymatic route, cyanide produced in vivo can be converted in part to thiocyanate by sulfur transferase systems. The thiocyanate ion can be oxidized at acid pH by hydrogen peroxide to generate sulfate and cyanide. The reaction is catalyzed by hemoglobin acting as a peroxidase; Thiocyanate is analogous to the cyanate ion, [OCN]-, wherein oxygen is replaced by sulfur. [SCN]- is one of the pseudohalides, due to the similarity of its reactions to that of halide ions. Thiocyanate used to be known as rhodanide (from a Greek word for rose) because of the red colour of its complexes with iron. Thiocyanate is produced by the reaction of elemental sulfur or thiosulfate with cyanide:; Thiocyanate shares its negative charge approximately equally between sulfur and nitrogen. As a consequence, thiocyanate can act as a nucleophile at either sulfur or nitrogen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | CNS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 58.082 Monoisotopic: 57.975144695 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-M | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/CHNS/c2-1-3/h3H/p-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | cyanosulfanide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | thiocyanate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | [S-]C#N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as thiocyanates. These are salts or esters of thiocyanic acid, with the general formula RSC#N (R=alkyl, aryl). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organosulfur compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Thiocyanates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Thiocyanates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Hydrogen cyanide + Thiosulfate > Hydrogen ion + Sulfite + Thiocyanate Hydrogen cyanide + 3-Mercaptopyruvic acid + Cyanide <> Hydrogen ion + Pyruvic acid + Thiocyanate Thiosulfate + Cyanide <> Sulfite + Thiocyanate Hydrogen cyanide + 3-Mercaptopyruvic acid <> Thiocyanate + Pyruvic acid Hydrogen cyanide + 3-Mercaptopyruvic acid Hydrogen ion + Pyruvic acid + Thiocyanate <i>S</i>-sulfanyl-[acceptor] + Hydrogen cyanide an unsulfurated sulfur acceptor + Thiocyanate + Hydrogen ion Thiosulfate + Hydrogen cyanide > Sulfite + Thiocyanate 3-Mercaptopyruvic acid + Hydrogen cyanide > Pyruvic acid + Thiocyanate Cyanide + Thiosulfate + Cyanide + Thiosulfate > Thiocyanate + Sulfite + Hydrogen ion + Thiocyanate + Sulfite Hydrogen cyanide + Thiosulfate > Thiocyanate + Sulfite +2 Hydrogen ion Thiosulfate + Cyanide <> Sulfite + Thiocyanate Thiosulfate + Cyanide <> Sulfite + Thiocyanate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes, although with low efficiency, the sulfur transfer reaction from thiosulfate to cyanide. The relatively low affinity of glpE for both thiosulfate and cyanide suggests that these compounds are not the physiological substrates. Thioredoxin 1 or related dithiol proteins could instead be the physiological sulfur-acceptor substrate. Possible association with the metabolism of glycerol-phosphate remains to be elucidated
- Gene Name:
- glpE
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6V5
- Molecular weight:
- 12082
Reactions
| Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Transfers a sulfur ion to cyanide or to other thiol compounds. Also has weak rhodanese activity (130-fold lower). Its participation in detoxification of cyanide may be small. May be involved in the enhancement of serine sensitivity
- Gene Name:
- sseA
- Uniprot ID:
- P31142
- Molecular weight:
- 30812
Reactions
| 3-mercaptopyruvate + cyanide = pyruvate + thiocyanate. |
- General function:
- Involved in thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate
- Gene Name:
- ynjE
- Uniprot ID:
- P78067
- Molecular weight:
- 48228
Reactions
| Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate. |
- General function:
- Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- The phage shock protein (psp) operon (pspABCDE) may play a significant role in the competition for survival under nutrient- or energy-limited conditions. PspE catalyzes the sulfur-transfer reaction from thiosulfate to cyanide, to form sulfite and thiocyanate. Also able to use dithiol (dithiothreitol) as an alternate sulfur acceptor. Also possesses a very low mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase activity
- Gene Name:
- pspE
- Uniprot ID:
- P23857
- Molecular weight:
- 11475
Reactions
| Thiosulfate + cyanide = sulfite + thiocyanate. |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Non-specific porin
- Gene Name:
- ompN
- Uniprot ID:
- P77747
- Molecular weight:
- 41220
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of inorganic phosphate, phosphorylated compounds, and some other negatively charged solutes
- Gene Name:
- phoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P02932
- Molecular weight:
- 38922
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- OmpF is a porin that forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane. It is also a receptor for the bacteriophage T2
- Gene Name:
- ompF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02931
- Molecular weight:
- 39333
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- ompC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06996
- Molecular weight:
- 40368