Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Lipid A-core (M2MDB001343)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 14:49:31 -0600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 17:20:10 -0600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Lipid A-core | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Lipid a-core belongs to the class of Polyhexoses. These are polysaccharides in which the saccharide units are hexoses. (inferred from compound structure) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a major component on the surface of Gram negative bacteria and is composed of lipid A-core and the O antigen polysaccharide. (PMID 20333251) WaaL is a membrane enzyme implicated in ligating undecaprenyl-diphosphate (Und-PP)-linked O antigen to lipid A-core oligosaccharide. (PMID 19019161) MsbA is an essential ATP-binding cassette half-transporter in the cytoplasmic membrane of the gram-negative Escherichia coli and is required for the export of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) to the outer membrane, most likely by transporting the lipid A core moiety. (PMID 16159769) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C162H296N2O89P4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 3819.9387 Monoisotopic: 3817.764804888 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | PIKXVLIJAUWPDI-VUQADABISA-P | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C162H294N2O89P4/c1-7-13-19-25-31-37-38-44-50-56-62-68-108(184)229-90(66-60-54-48-42-35-29-23-17-11-5)72-110(186)237-142-112(164-106(182)71-89(65-59-53-47-41-34-28-22-16-10-4)228-107(183)67-61-55-49-43-36-30-24-18-12-6)149(224-84-102-117(191)141(236-109(185)70-88(173)64-58-52-46-40-33-27-21-15-9-3)111(150(232-102)253-257(220,221)222)163-105(181)69-87(172)63-57-51-45-39-32-26-20-14-8-2)235-104(140(142)250-254(211,212)213)86-227-161(159(207)208)74-98(247-162(160(209)210)73-91(174)113(187)135(248-162)94(177)77-167)139(138(249-161)96(179)79-169)242-156-131(205)144(147(251-255(214,215)216)136(240-156)95(178)78-168)245-157-132(206)145(148(252-256(217,218)219)137(241-157)97(180)82-223-152-127(201)121(195)124(198)133(238-152)92(175)75-165)244-155-130(204)143(118(192)103(234-155)85-225-151-126(200)119(193)114(188)99(80-170)230-151)243-158-146(123(197)115(189)100(81-171)231-158)246-154-129(203)120(194)116(190)101(233-154)83-226-153-128(202)122(196)125(199)134(239-153)93(176)76-166/h87-104,111-158,160,165-180,187-206,209-210,214-219H,7-86H2,1-6H3,(H5-2,163,164,181,182,207,208,211,212,213,220,221,222)/p+2/t87-,88-,89-,90-,91-,92+,93+,94-,95+,96-,97+,98-,99-,100-,101-,102-,103-,104-,111-,112-,113-,114+,115-,116-,117-,118-,119+,120+,121+,122+,123+,124+,125+,126-,127+,128+,129-,130-,131+,132+,133?,134?,135-,136?,137?,138-,139-,140-,141-,142-,143?,144-,145-,146?,147-,148-,149-,150-,151?,152?,153?,154?,155?,156?,157?,158?,161-,162-/m1/s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | {[(3R,4R,5S)-6-{[(2R,3R,4R,6R)-6-carboxy-2-[(1R)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-{[(2R,4R,5R,6R)-6-[(1R)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-2-(dihydroxymethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-6-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-5-{[(3R)-1,3-dihydroxytetradecylidene]amino}-3-hydroxy-4-{[(3R)-3-hydroxytetradecanoyl]oxy}-6-(phosphonooxy)oxan-2-yl]methoxy}-5-{[(3R)-3-(dodecanoyloxy)-1-hydroxytetradecylidene]amino}-3-(phosphonooxy)-4-{[(3R)-3-(tetradecanoyloxy)tetradecanoyl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]methoxy}oxan-3-yl]oxy}-2-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-{[(3S,4R,5R)-6-[(1S)-2-{[(3S,4S,5S)-6-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-{[(3R,5R,6R)-4-{[(4S,5S,6R)-3-{[(3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-({[(3S,4S,5S)-6-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,5-dihydroxy-6-({[(3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-hydroxy-5-[(trihydroxyphosphaniumyl)oxy]oxan-2-yl]oxy}-5-hydroxyoxan-3-yl]oxy}trihydroxyphosphanium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | {[(3R,4R,5S)-6-{[(2R,3R,4R,6R)-6-carboxy-2-[(1R)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-{[(2R,4R,5R,6R)-6-[(1R)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-2-(dihydroxymethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-6-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R,6R)-5-{[(3R)-1,3-dihydroxytetradecylidene]amino}-3-hydroxy-4-{[(3R)-3-hydroxytetradecanoyl]oxy}-6-(phosphonooxy)oxan-2-yl]methoxy}-5-{[(3R)-3-(dodecanoyloxy)-1-hydroxytetradecylidene]amino}-3-(phosphonooxy)-4-{[(3R)-3-(tetradecanoyloxy)tetradecanoyl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]methoxy}oxan-3-yl]oxy}-2-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-{[(3S,4R,5R)-6-[(1S)-2-{[(3S,4S,5S)-6-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-{[(3R,5R,6R)-4-{[(4S,5S,6R)-3-{[(3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-({[(3S,4S,5S)-6-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,5-dihydroxy-6-({[(3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-hydroxy-5-[(trihydroxyphosphaniumyl)oxy]oxan-2-yl]oxy}-5-hydroxyoxan-3-yl]oxy}trihydroxyphosphanium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
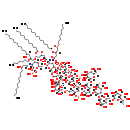
| SMILES: | [H][C@@](O)(CCCCCCCCCCC)CC(=O)O[C@@]1([H])[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]([H])(CO[C@]2([H])O[C@]([H])(CO[C@@]3(C[C@@]([H])(O[C@@]4(C[C@@]([H])(O)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O4)[C@]([H])(O)CO)C(O)O)[C@@]([H])(OC4([H])OC([H])([C@@]([H])(O)CO)[C@@]([H])(O[P+](O)(O)O)[C@]([H])(OC5([H])OC([H])([C@@]([H])(O)COC6([H])OC([H])([C@@]([H])(O)CO)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@]6([H])O)[C@@]([H])(O[P+](O)(O)O)[C@]([H])(OC6([H])O[C@]([H])(COC7([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]7([H])O)[C@@]([H])(O)C([H])(OC7([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)C7([H])OC7([H])O[C@]([H])(COC8([H])OC([H])([C@@]([H])(O)CO)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@]8([H])O)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]7([H])O)[C@@]6([H])O)[C@]5([H])O)[C@]4([H])O)[C@]([H])(O3)[C@]([H])(O)CO)C(O)=O)[C@@]([H])(OP(O)(O)=O)[C@]([H])(OC(=O)C[C@@]([H])(CCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCC)[C@@]2([H])N=C(O)C[C@@]([H])(CCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCC)O[C@]([H])(OP(O)(O)=O)[C@]1([H])N=C(O)C[C@]([H])(O)CCCCCCCCCCC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as saccharolipids. Saccharolipids are compounds in which fatty acids are linked directly to a sugar backbone, forming structures that are compatible with membrane bilayers. In the saccharolipids, a sugar substitutes for the glycerol backbone that is present in glycerolipids and glycerophospholipids. The most familiar saccharolipids contain an acylated glucosamine. In contrast to others glycolipids, the fatty acid is not glycosidically linked to the sugar moiety. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Saccharolipids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Saccharolipids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Membrane | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Lipid A-core + colanic acid > M<sub>LPS</sub> Hydrogen ion + Lipid A-core + Undecaprenyl diphosphate lipid A-core 1-diphosphate + Di-trans,poly-cis-undecaprenyl phosphate Galactosyl-glucosyl3-heptosyl3-KDO2-lipid A-bisphosphate + ADP-L-Glycero-D-manno-heptose > Hydrogen ion + Lipid A-core + ADP galactosyl-(glucosyl)3-(heptosyl)3-Kdo2-lipid A-bisphosphate + ADP-L-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose > Hydrogen ion + Adenosine diphosphate + Lipid A-core + ADP Lipid A-core + Adenosine triphosphate + Water > Adenosine diphosphate + Phosphate + Hydrogen ion + Lipid A-core + ADP Lipid A-core + Adenosine triphosphate + Water > Adenosine diphosphate + Phosphate + Hydrogen ion + Lipid A-core + ADP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
- Specific function:
- Adds the O-antigen on the glucose group of LPS
- Gene Name:
- rfaL
- Uniprot ID:
- P27243
- Molecular weight:
- 46877
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groups
- Specific function:
- Adds the terminal N-acetyl-D-glucosamine group on the glucose(II) group of LPS
- Gene Name:
- waaU
- Uniprot ID:
- P27242
- Molecular weight:
- 41729
Reactions
| UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + lipopolysaccharide = UDP + N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyllipopolysaccharide. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in lipid A export and possibly also in glycerophospholipid export and for biogenesis of the outer membrane. Transmembrane domains (TMD) form a pore in the inner membrane and the ATP-binding domain (NBD) is responsible for energy generation
- Gene Name:
- msbA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60752
- Molecular weight:
- 64460
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- yeiU
- Uniprot ID:
- P76445
- Molecular weight:
- 26759
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in lipid A export and possibly also in glycerophospholipid export and for biogenesis of the outer membrane. Transmembrane domains (TMD) form a pore in the inner membrane and the ATP-binding domain (NBD) is responsible for energy generation
- Gene Name:
- msbA
- Uniprot ID:
- P60752
- Molecular weight:
- 64460