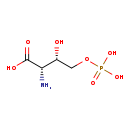Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine (M2MDB000691)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 14:09:27 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 15:54:54 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine is involved in the vitamin B6 metabolism system. O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine is a precursor for pyridoxine. O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine can be converted to 4-hydroxy-L-threonine and 2-Amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutyrate by threonine synthase [EC:4.2.3.1] and 4-hydroxythreonine-4-phosphate dehydrogenase [EC:1.1.1.262], respectively. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C4H10NO7P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 215.0985 Monoisotopic: 215.019488191 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | FKHAKIJOKDGEII-GBXIJSLDSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C4H10NO7P/c5-3(4(7)8)2(6)1-12-13(9,10)11/h2-3,6H,1,5H2,(H,7,8)(H2,9,10,11)/t2-,3+/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2S,3S)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)butanoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | 4-(phosphonooxy)-L-threonine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | N[C@@H]([C@H](O)COP(O)(O)=O)C(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | L-alpha-amino acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + NAD + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine > Carbon dioxide + Hydrogen ion +2 Water + NADH + Pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + Phosphate Water + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine > 4-Hydroxy-L-threonine + Phosphate L-Glutamate + 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid <> alpha-Ketoglutarate + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + alpha-Ketoglutarate <> 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid + L-Glutamate O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + Water <> 4-Hydroxy-L-threonine + Phosphate O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + NAD <> 2-Amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutyrate + NADH + Hydrogen ion O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + NAD > Hydrogen ion + NADH + 2-Amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutyrate 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid + L-Glutamate <> O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + Oxoglutaric acid 4-Hydroxy-L-threonine + Adenosine triphosphate > Hydrogen ion + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + ADP O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + NAD > 2-Amino-3-phosphonopropionic acid + Carbon dioxide + NADH O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + Oxoglutaric acid > 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid + L-Glutamate Phosphoserine + alpha-Ketoglutarate + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine <> Phosphohydroxypyruvic acid + L-Glutamate + 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid NAD + 2-Amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutyrate + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine <> 3-Amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate + Carbon dioxide + NADH + Hydrogen ion 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid + L-Glutamic acid + L-Glutamate <> A-Ketoglutaric acid oxime + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine L-Glutamic acid + L-Glutamate <> O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine L-Glutamic acid + L-Glutamate <> Oxoglutaric acid + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine L-Glutamic acid + L-Glutamate <> O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + A-Ketoglutaric acid oxime 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid + L-Glutamic acid + L-Glutamate <> O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + Oxoglutaric acid O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + NAD <>2 2-Amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutyrate + NADH + Hydrogen ion L-Glutamate + 2 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-4-phosphobutanoic acid <> alpha-Ketoglutarate + O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine O-Phospho-4-hydroxy-L-threonine + NAD <>2 2-Amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutyrate + NADH + Hydrogen ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the gamma-elimination of phosphate from L- phosphohomoserine and the beta-addition of water to produce L- threonine. To a lesser extent, is able to slowly catalyze the deamination of L-threonine into alpha-ketobutyrate and that of L- serine and 3-chloroalanine into pyruvate. Is also able to rapidly convert vinylglycine to threonine, which proves that the pyridoxal p-quinonoid of vinylglycine is an intermediate in the TS reaction
- Gene Name:
- thrC
- Uniprot ID:
- P00934
- Molecular weight:
- 47113
Reactions
| O-phospho-L-homoserine + H(2)O = L-threonine + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the complicated ring closure reaction between the two acyclic compounds 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) and 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate (1-amino-acetone-3-phosphate or AAP) to form pyridoxine 5'-phosphate (PNP) and inorganic phosphate
- Gene Name:
- pdxJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A794
- Molecular weight:
- 26384
Reactions
| 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate = pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + phosphate + 2 H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in 4-hydroxythreonine-4-phosphate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NAD(P)-dependent oxidation of 4- (phosphohydroxy)-L-threonine (HTP) into 2-amino-3-oxo-4- (phosphohydroxy)butyric acid which spontaneously decarboxylates to form 3-amino-2-oxopropyl phosphate (AHAP)
- Gene Name:
- pdxA
- Uniprot ID:
- P19624
- Molecular weight:
- 35114
Reactions
| 4-(phosphonooxy)-L-threonine + NAD(+) = (2S)-2-amino-3-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in metabolic process
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reversible conversion of 3- phosphohydroxypyruvate to phosphoserine and of 3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4- phosphonooxybutanoate to phosphohydroxythreonine. Is involved in both pyridoxine and serine biosynthesis
- Gene Name:
- serC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23721
- Molecular weight:
- 39783
Reactions
| O-phospho-L-serine + 2-oxoglutarate = 3-phosphonooxypyruvate + L-glutamate. |
| 4-phosphonooxy-L-threonine + 2-oxoglutarate = (3R)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4-phosphonooxybutanoate + L-glutamate. |