Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Shikimic acid (M2MDB000477)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 13:57:48 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-09-13 12:56:12 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
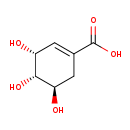
| Name: | Shikimic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower shikimi ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C7H10O5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 174.1513 Monoisotopic: 174.05282343 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | JXOHGGNKMLTUBP-HSUXUTPPSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C7H10O5/c8-4-1-3(7(11)12)2-5(9)6(4)10/h1,4-6,8-10H,2H2,(H,11,12)/t4-,5-,6-/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 138-59-0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxycyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | (-)-shikimate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | O[C@@H]1CC(=C[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)C(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as shikimic acids and derivatves. These are cyclitols containing a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid substituted with three hydroxyl groups at positions 3, 4, and 5. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Alcohols and polyols | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Shikimic acids and derivatves | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 186 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | 3-Dehydro-shikimate + Hydrogen ion + NADPH <> NADP + Shikimic acid Adenosine triphosphate + Shikimic acid <> ADP + Hydrogen ion + Shikimate 3-phosphate Adenosine triphosphate + Shikimic acid <> ADP + Shikimate 3-phosphate Shikimic acid + NADP <> 3-Dehydro-shikimate + NADPH + Hydrogen ion Shikimic acid + NAD <> 3-Dehydro-shikimate + NADH + Hydrogen ion NAD(P)<sup>+</sup> + Shikimic acid < NAD(P)H + 3-Dehydro-shikimate + Hydrogen ion NADP + Shikimic acid < Hydrogen ion + NADPH + 3-Dehydro-shikimate Shikimic acid + Adenosine triphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Shikimate 3-phosphate + ADP Shikimic acid + NADP > 3-dehydroshikimate + NADPH Adenosine triphosphate + Shikimic acid > ADP + Shikimate 3-phosphate Shikimic acid + NAD(P)(+) > 3-dehydroshikimate + NAD(P)H Quinate + NAD + NADP + Shikimic acid <> 3-Dehydroquinate + NADH + NADPH + Hydrogen ion + 3-Dehydro-shikimate 3-dehydroshikimate + Hydrogen ion + NADPH + 3-Dehydro-shikimate + NADPH > NADP + Shikimic acid Shikimic acid + Adenosine triphosphate > Adenosine diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + shikimate 3-phosphate + ADP + Shikimate 3-phosphate 3 3-Dehydro-shikimate + Hydrogen ion + NADPH <> NADP + Shikimic acid Adenosine triphosphate + Shikimic acid <> ADP + Hydrogen ion + Shikimate 3-phosphate 3 3-Dehydro-shikimate + Hydrogen ion + NADPH <> NADP + Shikimic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Find out more about how we convert literature concentrations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- The physiological substrate is not known
- Gene Name:
- ydiB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6D5
- Molecular weight:
- 31228
Reactions
| L-quinate + NAD(P)(+) = 3-dehydroquinate + NAD(P)H. |
| Shikimate + NAD(P)(+) = 3-dehydroshikimate + NAD(P)H. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of the 3-hydroxyl group of shikimic acid using ATP as a cosubstrate
- Gene Name:
- aroK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6D7
- Molecular weight:
- 19538
Reactions
| ATP + shikimate = ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in shikimate kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the specific phosphorylation of the 3-hydroxyl group of shikimic acid using ATP as a cosubstrate
- Gene Name:
- aroL
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A6E1
- Molecular weight:
- 19151
Reactions
| ATP + shikimate = ADP + shikimate 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Shikimate + NADP(+) = 3-dehydroshikimate + NADPH
- Gene Name:
- aroE
- Uniprot ID:
- P15770
- Molecular weight:
- 29413
Reactions
| Shikimate + NADP(+) = 3-dehydroshikimate + NADPH. |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Specific function unknown
- Gene Name:
- shiA
- Uniprot ID:
- P76350
- Molecular weight:
- 47817
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Non-specific porin
- Gene Name:
- ompN
- Uniprot ID:
- P77747
- Molecular weight:
- 41220
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of inorganic phosphate, phosphorylated compounds, and some other negatively charged solutes
- Gene Name:
- phoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P02932
- Molecular weight:
- 38922
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- OmpF is a porin that forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane. It is also a receptor for the bacteriophage T2
- Gene Name:
- ompF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02931
- Molecular weight:
- 39333
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- ompC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06996
- Molecular weight:
- 40368