Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Flavin Mononucleotide (M2MDB000408)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 13:53:53 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-09-13 12:56:11 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
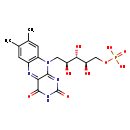
| Name: | Flavin Mononucleotide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | FMN is coenzyme for a number of oxidative enzymes including NADH dehydrogenase. It is the principal form in which riboflavin is found in cells. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C17H21N4O9P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 456.3438 Monoisotopic: 456.104614802 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | FVTCRASFADXXNN-SCRDCRAPSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C17H21N4O9P/c1-7-3-9-10(4-8(7)2)21(15-13(18-9)16(25)20-17(26)19-15)5-11(22)14(24)12(23)6-30-31(27,28)29/h3-4,11-12,14,22-24H,5-6H2,1-2H3,(H,20,25,26)(H2,27,28,29)/t11-,12+,14-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 146-17-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | {[(2R,3S,4S)-5-{7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-2H,3H,4H,10H-benzo[g]pteridin-10-yl}-2,3,4-trihydroxypentyl]oxy}phosphonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | riboflavin 5'-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | CC1=CC2=C(C=C1C)N(C[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)COP(O)(O)=O)C1=NC(=O)NC(=O)C1=N2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as flavin nucleotides. These are nucleotides containing a flavin moiety. Flavin is a compound that contains the tricyclic isoalloxazine ring system, which bears 2 oxo groups at the 2- and 4-positions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Flavin nucleotides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Flavin nucleotides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 290 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + NADH > FMNH + NAD Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + NADPH <> FMNH + NADP Adenosine triphosphate + Riboflavin <> ADP + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Adenosine triphosphate + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion > FAD + Pyrophosphate FMNH + Oxygen + Sulfoacetate > Flavin Mononucleotide + Glyoxylic acid + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite FMNH + Isethionic acid + Oxygen > Flavin Mononucleotide + Glycolaldehyde + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite FMNH + Methanesulfonate + Oxygen > Formaldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite Butanesulfonate + FMNH + Oxygen > Butanal + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite Ethanesulfonate + FMNH + Oxygen > Acetaldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite 2 Ferroxamine + FMNH >2 Iron +2 ferroxamine minus Fe(3) + Flavin Mononucleotide +2 Hydrogen ion Adenosine triphosphate + Flavin Mononucleotide <> Pyrophosphate + FAD Flavin Mononucleotide + Water <> Riboflavin + Phosphate Adenosine triphosphate + Riboflavin <> ADP + Flavin Mononucleotide FMNH + NAD <> Flavin Mononucleotide + NADH + Hydrogen ion FMNH + NADP <> Flavin Mononucleotide + NADPH + Hydrogen ion Uracil + FMNH + Oxygen <> Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide NAD(P)<sup>+</sup> + FMNH <> NAD(P)H + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Riboflavin + Adenosine triphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Flavin Mononucleotide + ADP FMNH + NADP < Flavin Mononucleotide + NADPH + Hydrogen ion Thymine + Oxygen + FMNH > (<i>Z</i>)-2-methylureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion an alkanesulfonate + Oxygen + FMNH > an aldehyde + Sulfite + Water + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Flavin Mononucleotide + Water > Riboflavin + Phosphate Uracil + Oxygen + FMNH > Hydrogen ion + Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide Butanesulfonate + Oxygen + FMNH > Butanal + Sulfite + Water + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Adenosine triphosphate + Riboflavin > ADP + Flavin Mononucleotide Adenosine triphosphate + Flavin Mononucleotide > Pyrophosphate + FAD More...Uracil + FMNH(2) + Oxygen > Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + Water Thymine + FMNH(2) + Oxygen > (Z)-2-Methyl-ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + Water FMNH(2) + NAD > Flavin Mononucleotide + NADH An alkanesufonate (R-CH(2)-SO(3)H) + FMNH(2) + Oxygen > an aldehyde (R-CHO) + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Water FMNH(2) + NADP > Flavin Mononucleotide + NADPH Alkanesulfonate + FMNH + Oxygen <> Aldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Water Uracil + FMNH + Oxygen + Thymine <> Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + (Z)-2-Methyl-ureidoacrylate peracid alkylsulfonate + FMNH2 + Oxygen > Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite + Flavin Mononucleotide + Water +2 Hydrogen ion + Sulfite Butanesulfonate + Oxygen + FMNH2 > Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite + Flavin Mononucleotide + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite Oxygen + FMNH2 + 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonate > Sulfite + Water + Hydrogen ion + Flavin Mononucleotide + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite ethanesulfonate + Oxygen + FMNH2 > Hydrogen ion + Water + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite isethionate + Oxygen + FMNH2 > Betaine aldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Water + Sulfite + Sulfite Oxygen + methanesulfonate + FMNH2 + Methanesulfonate > Hydrogen ion + Water + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Betaine aldehyde + Sulfite Riboflavin + Adenosine triphosphate + Riboflavin > Adenosine diphosphate + Hydrogen ion + Flavin Mononucleotide + ADP Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Adenosine triphosphate > Pyrophosphate + FAD Uracil + FMNH2 + Oxygen > Ureidoacrylate peracid + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + Peroxyaminoacrylate Alkanesulfonate + FMNH + Oxygen <> Aldehyde + Flavin Mononucleotide + Sulfite + Water Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + NADH > FMNH + NAD Adenosine triphosphate + Riboflavin <> ADP + Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion Flavin Mononucleotide + Hydrogen ion + NADH > FMNH + NAD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Find out more about how we convert literature concentrations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Ono, Shigeru; Hirano, Hiroko; Sato, Yoshiyuki. Formation of flavin adenine dinucleotide and flavin mononucleotide by lens homogenate. Experimental Eye Research (1982), 34(2), 297-301. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate
- Gene Name:
- appA
- Uniprot ID:
- P07102
- Molecular weight:
- 47056
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate. |
| Myo-inositol hexakisphosphate + H(2)O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,2,3,5,6-pentakisphosphate + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Dephosphorylates several organic phosphomonoesters and catalyzes the transfer of low-energy phosphate groups from phosphomonoesters to hydroxyl groups of various organic compounds. Preferentially acts on aryl phosphoesters. Might function as a broad-spectrum dephosphorylating enzyme able to scavenge both 3'- and 5'-nucleotides and also additional organic phosphomonoesters
- Gene Name:
- aphA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AE22
- Molecular weight:
- 26103
Reactions
| A phosphate monoester + H(2)O = an alcohol + phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the reduction of soluble flavins by reduced pyridine nucleotides. Seems to reduces the complexed Fe(3+) iron of siderophores to Fe(2+), thus releasing it from the chelator
- Gene Name:
- fre
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEN1
- Molecular weight:
- 26242
Reactions
| Reduced riboflavin + NAD(P)(+) = riboflavin + NAD(P)H. |
| 2 cob(II)alamin + NAD(+) = 2 aquacob(III)alamin + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in FMN adenylyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + riboflavin = ADP + FMN
- Gene Name:
- ribF
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AG40
- Molecular weight:
- 34734
Reactions
| ATP + riboflavin = ADP + FMN. |
| ATP + FMN = diphosphate + FAD. |
- General function:
- Involved in sulfite reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the sulfite reductase complex that catalyzes the 6-electron reduction of sulfite to sulfide. This is one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L- cysteine from sulfate
- Gene Name:
- cysI
- Uniprot ID:
- P17846
- Molecular weight:
- 63998
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O = sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in sulfite reductase (NADPH) activity
- Specific function:
- Component of the sulfite reductase complex that catalyzes the 6-electron reduction of sulfite to sulfide. This is one of several activities required for the biosynthesis of L- cysteine from sulfate. The flavoprotein component catalyzes the electron flow from NADPH -> FAD -> FMN to the hemoprotein component
- Gene Name:
- cysJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P38038
- Molecular weight:
- 66269
Reactions
| H(2)S + 3 NADP(+) + 3 H(2)O = sulfite + 3 NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding
- Specific function:
- Involved in the reduction of ferric iron in cytoplasmic ferrioxamine B
- Gene Name:
- fhuF
- Uniprot ID:
- P39405
- Molecular weight:
- 30113
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the dephosphorylation of the artificial chromogenic substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) and of the natural substrates FMN and beta-glucose 1-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- ybjI
- Uniprot ID:
- P75809
- Molecular weight:
- 30196
- General function:
- Involved in FMN reductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes an NAD(P)H-dependent reduction of FMN, but is also able to reduce FAD or riboflavin
- Gene Name:
- ssuE
- Uniprot ID:
- P80644
- Molecular weight:
- 21253
Reactions
| FMNH(2) + NADP(+) = FMN + NADPH. |
- General function:
- Involved in alkanesulfonate monooxygenase activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in desulfonation of aliphatic sulfonates. Catalyzes the conversion of pentanesulfonic acid to sulfite and pentaldehyde and is able to desulfonate a wide range of sulfonated substrates including C-2 to C-10 unsubstituted linear alkanesulfonates, substituted ethanesulfonic acids and sulfonated buffers
- Gene Name:
- ssuD
- Uniprot ID:
- P80645
- Molecular weight:
- 41736
Reactions
| An alkanesufonate (R-CH(2)-SO(3)H) + FMNH(2) + O(2) = an aldehyde (R-CHO) + FMN + sulfite + H(2)O. |
- General function:
- Involved in FMN binding
- Specific function:
- Makes part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutF
- Uniprot ID:
- P75893
- Molecular weight:
- 17749
Reactions
| FMNH(2) + NAD(+) = FMN + NADH. |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen
- Specific function:
- Part of the rut operon, which is required for the utilization of pyrimidines as sole nitrogen source
- Gene Name:
- rutA
- Uniprot ID:
- P75898
- Molecular weight:
- 42219
Reactions
| Uracil + FMNH(2) + O(2) = (Z)-3-ureidoacrylate peracid + FMN + H(2)O. |
| Thymine + FMNH(2) + O(2) = (Z)-2-methylureidoacrylate peracid + FMN + H(2)O. |