Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Fructose 1-phosphate (M2MDB000243)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 13:44:38 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-06-03 15:53:42 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Fructose 1-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Fructose 1-phosphate is an intermediate metabolite in the Fructose and mannose metabolism pathway. It is generated by fructokinase and it is broken down by aldolase B into glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
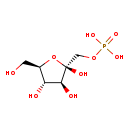
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C6H13O9P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 260.1358 Monoisotopic: 260.029718526 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | RHKKZBWRNHGJEZ-ARQDHWQXSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C6H13O9P/c7-1-3-4(8)5(9)6(10,15-3)2-14-16(11,12)13/h3-5,7-10H,1-2H2,(H2,11,12,13)/t3-,4-,5+,6-/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 15978-08-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | {[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | [(2R,3S,4S,5R)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxyphosphonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | OC[C@H]1O[C@](O)(COP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hexose phosphates. These are carbohydrate derivatives containing a hexose substituted by one or more phosphate groups. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Hexose phosphates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Phosphoenolpyruvic acid + D-Fructose > Fructose 1-phosphate + Pyruvic acid Adenosine triphosphate + Fructose 1-phosphate > ADP + Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + Hydrogen ion Adenosine triphosphate + Fructose 1-phosphate <> ADP + beta-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Fructose 1-phosphate <> Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + D-Glyceraldehyde Protein N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine + D-Fructose <> Protein histidine + Fructose 1-phosphate Fructose 1-phosphate + Water > D-fructose + Phosphate D-fructose + Phosphoenolpyruvic acid > Fructose 1-phosphate + Pyruvic acid Adenosine triphosphate + Fructose 1-phosphate > ADP + Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Adenosine triphosphate + Fructose 1-phosphate <> ADP + beta-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Hara, Yoshito. Ion exchange separation of fructose 1-phosphate by using borate as the eluant. Journal of Biochemistry (Tokyo, Japan) (1959), 46 571-3. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups
- Specific function:
- General (non sugar-specific) component of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS). This major carbohydrate active-transport system catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. Enzyme I transfers the phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to the phosphoryl carrier protein (HPr)
- Gene Name:
- ptsI
- Uniprot ID:
- P08839
- Molecular weight:
- 63561
Reactions
| Phosphoenolpyruvate + protein L-histidine = pyruvate + protein N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = glycerone phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
- Gene Name:
- fbaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A991
- Molecular weight:
- 38109
Reactions
| D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = glycerone phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the aldol condensation of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP or glycerone-phosphate) with glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate (G3P) to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) in gluconeogenesis and the reverse reaction in glycolysis
- Gene Name:
- fbaA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AB71
- Molecular weight:
- 39147
Reactions
| D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = glycerone phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 1-phosphofructokinase activity
- Specific function:
- ATP + D-fructose 1-phosphate = ADP + D- fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
- Gene Name:
- fruK
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEW9
- Molecular weight:
- 33755
Reactions
| ATP + D-fructose 1-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in sugar:hydrogen symporter activity
- Specific function:
- The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS), a major carbohydrate active -transport system, catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. This system is involved in fructose transport
- Gene Name:
- fruA
- Uniprot ID:
- P20966
- Molecular weight:
- 57519
Reactions
| Protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine + sugar = protein EIIB + sugar phosphate. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS), a major carbohydrate active -transport system, catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. This system is involved in fructose transport
- Gene Name:
- fruB
- Uniprot ID:
- P69811
- Molecular weight:
- 39647
Reactions
| Protein EIIA N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine + protein EIIB = protein EIIA + protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine. |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the dephosphorylation of the artificial chromogenic substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) and of the natural substrates fructose 1-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate
- Gene Name:
- yqaB
- Uniprot ID:
- P77475
- Molecular weight:
- 20780
- General function:
- Involved in sugar:hydrogen symporter activity
- Specific function:
- General (non sugar-specific) component of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS). This major carbohydrate active-transport system catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. The phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is transferred to the phosphoryl carrier protein HPr by enzyme I. Phospho-HPr then transfers it to the permease (enzymes II/III)
- Gene Name:
- ptsH
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AA04
- Molecular weight:
- 9119
Reactions
| Protein HPr N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine + protein EIIA = protein HPr + protein EIIA N(tau)-phospho-L-histidine. |
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in sugar:hydrogen symporter activity
- Specific function:
- The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system (sugar PTS), a major carbohydrate active -transport system, catalyzes the phosphorylation of incoming sugar substrates concomitantly with their translocation across the cell membrane. This system is involved in fructose transport
- Gene Name:
- fruA
- Uniprot ID:
- P20966
- Molecular weight:
- 57519
Reactions
| Protein EIIB N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine/cysteine + sugar = protein EIIB + sugar phosphate. |