Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Ureidosuccinic acid (M2MDB000189)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 13:01:23 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-09-13 12:56:09 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Ureidosuccinic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Ureidosuccinic acid is an intermediary product in pyrimidine metabolism. It is generated by the action of dihydroorotase which catalyzes the following reaction: 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Water <=> Ureidosuccinic acid + H+ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
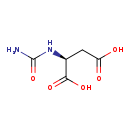
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C5H8N2O5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 176.1274 Monoisotopic: 176.043321376 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | HLKXYZVTANABHZ-REOHCLBHSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C5H8N2O5/c6-5(12)7-2(4(10)11)1-3(8)9/h2H,1H2,(H,8,9)(H,10,11)(H3,6,7,12)/t2-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 13184-27-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | (2S)-2-(carbamoylamino)butanedioic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | carbamylaspartic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | NC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aspartic acid and derivatives. Aspartic acid and derivatives are compounds containing an aspartic acid or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of aspartic acid at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Aspartic acid and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | -2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | 174 - 175 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | L-Aspartic acid + Carbamoylphosphate <> Ureidosuccinic acid + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Water <> Ureidosuccinic acid + Hydrogen ion Carbamoylphosphate + L-Aspartic acid <> Phosphate + Ureidosuccinic acid 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Water <> Ureidosuccinic acid L-Aspartic acid + Carbamoylphosphate > Hydrogen ion + Ureidosuccinic acid + Phosphate Carbamoylphosphate + L-Aspartic acid > Inorganic phosphate + Ureidosuccinic acid (S)-dihydroorotate + Water > Ureidosuccinic acid L-Aspartic acid + Carbamoylphosphate <> Ureidosuccinic acid + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate 4 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid + Water <> Ureidosuccinic acid + Hydrogen ion L-Aspartic acid + Carbamoylphosphate <> Ureidosuccinic acid + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Find out more about how we convert literature concentrations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O = N-carbamoyl-L- aspartate
- Gene Name:
- pyrC
- Uniprot ID:
- P05020
- Molecular weight:
- 38827
Reactions
| (S)-dihydroorotate + H(2)O = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in carboxyl- or carbamoyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = phosphate + N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
- Gene Name:
- pyrB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A786
- Molecular weight:
- 34427
Reactions
| Carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = phosphate + N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate. |
- General function:
- Involved in 'de novo' pyrimidine base biosynthetic process
- Specific function:
- Involved in allosteric regulation of aspartate carbamoyltransferase
- Gene Name:
- pyrI
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7F3
- Molecular weight:
- 17121