Structural search and advanced query search is temporarily unavailable. We are working to fix this issue. Thank you for your support and patience.
Cysteinylglycine (M2MDB000028)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-05-31 09:56:47 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2015-09-13 12:56:06 -0600 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name: | Cysteinylglycine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Cysteinylglycine is a naturally occurring dipeptide. It is derived from the breakdown of glutathione (a tripeptide). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
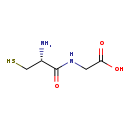
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula: | C5H10N2O3S | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weight: | Average: 178.21 Monoisotopic: 178.041212886 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key: | ZUKPVRWZDMRIEO-VKHMYHEASA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI: | InChI=1S/C5H10N2O3S/c6-3(2-11)5(10)7-1-4(8)9/h3,11H,1-2,6H2,(H,7,10)(H,8,9)/t3-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number: | 19246-18-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name: | 2-[(2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanamido]acetic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional IUPAC Name: | Cys-Gly | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES: | N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)NCC(O)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dipeptides. These are organic compounds containing a sequence of exactly two alpha-amino acids joined by a peptide bond. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Dipeptides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State: | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge: | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations: | Cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reactions: | Cysteinylglycine + Water > L-Cysteine + Glycine Adenosine triphosphate + Water + Cysteinylglycine > ADP + Cysteinylglycine + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate Adenosine triphosphate + Water + Cysteinylglycine > ADP + Cysteinylglycine + Hydrogen ion + Phosphate Glutathione + Water > Cysteinylglycine + L-Glutamate Glutathione + Water <> Cysteinylglycine + L-Glutamate Cysteinylglycine + Water <> L-Cysteine + Glycine Glutathione + L-Amino acid <> Cysteinylglycine + (5-L-Glutamyl)-L-amino acid Glutathione + Water > Cysteinylglycine + L-Glutamate Cysteinylglycine + Water > L-Cysteine + Glycine Glutathione + Water > Cysteinylglycine + L-Glutamate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMPDB Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Pathways: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoCyc Pathways: | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference: | Holleman, James W. Synthesis of glutathione and cysteinylglycine by soluble enzymes of rat liver. Compt. rend. (1954), 238 1360-1. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in proteolysis
- Specific function:
- Aminopeptidase N is involved in the degradation of intracellular peptides generated by protein breakdown during normal growth as well as in response to nutrient starvation
- Gene Name:
- pepN
- Uniprot ID:
- P04825
- Molecular weight:
- 98918
Reactions
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, Xaa-|-Yaa- from a peptide, amide or arylamide. Xaa is preferably Ala, but may be most amino acids including Pro (slow action). When a terminal hydrophobic residue is followed by a prolyl residue, the two may be released as an intact Xaa-Pro dipeptide. |
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- Dipeptidase with broad substrate specificity. Requires dipeptide substrates with an unblocked N-terminus and the amino group in the alpha or beta position. Non-protein amino acids and proline are not accepted in the C-terminal position, whereas some dipeptide amides and formyl amino acids are hydrolyzed. Also shows cysteinylglycinase activity, which is sufficient for E.coli to utilize cysteinylglycine as a cysteine source
- Gene Name:
- pepD
- Uniprot ID:
- P15288
- Molecular weight:
- 52915
Reactions
| Hydrolysis of dipeptides, preferentially hydrophobic dipeptides including prolyl amino acids. |
- General function:
- Involved in gamma-glutamyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- (5-L-glutamyl)-peptide + an amino acid = peptide + 5-L-glutamyl amino acid
- Gene Name:
- ggt
- Uniprot ID:
- P18956
- Molecular weight:
- 61768
Reactions
| A (5-L-glutamyl)-peptide + an amino acid = a peptide + a 5-L-glutamyl amino acid. |
| Glutathione + H(2)O = L-cysteinylglycine + L-glutamate. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminopeptidase activity
- Specific function:
- Probably plays an important role in intracellular peptide degradation
- Gene Name:
- pepB
- Uniprot ID:
- P37095
- Molecular weight:
- 46180
Reactions
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, Xaa, from a peptide or arylamide. Xaa is preferably Glu or Asp but may be other amino acids, including Leu, Met, His, Cys and Gln. |
- General function:
- Involved in aminopeptidase activity
- Specific function:
- Presumably involved in the processing and regular turnover of intracellular proteins. Catalyzes the removal of unsubstituted N-terminal amino acids from various peptides. Required for plasmid ColE1 site-specific recombination but not in its aminopeptidase activity. Could act as a structural component of the putative nucleoprotein complex in which the Xer recombination reaction takes place
- Gene Name:
- pepA
- Uniprot ID:
- P68767
- Molecular weight:
- 54879
Reactions
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, Xaa-|-Yaa-, in which Xaa is preferably Leu, but may be other amino acids including Pro although not Arg or Lys, and Yaa may be Pro. Amino acid amides and methyl esters are also readily hydrolyzed, but rates on arylamides are exceedingly low. |
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, preferentially leucine, but not glutamic or aspartic acids. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEF8
- Molecular weight:
- 37497
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEG1
- Molecular weight:
- 32308
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH2
- Molecular weight:
- 33443
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH6
- Molecular weight:
- 33022
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG0
- Molecular weight:
- 35844
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37313
- Molecular weight:
- 37560
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Dipeptide-binding protein of a transport system that can be subject to osmotic shock. DppA is also required for peptide chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- dppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23847
- Molecular weight:
- 60293
Transporters
- General function:
- Involved in proteolysis
- Specific function:
- Aminopeptidase N is involved in the degradation of intracellular peptides generated by protein breakdown during normal growth as well as in response to nutrient starvation
- Gene Name:
- pepN
- Uniprot ID:
- P04825
- Molecular weight:
- 98918
Reactions
| Release of an N-terminal amino acid, Xaa-|-Yaa- from a peptide, amide or arylamide. Xaa is preferably Ala, but may be most amino acids including Pro (slow action). When a terminal hydrophobic residue is followed by a prolyl residue, the two may be released as an intact Xaa-Pro dipeptide. |
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEF8
- Molecular weight:
- 37497
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- dppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AEG1
- Molecular weight:
- 32308
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH2
- Molecular weight:
- 33443
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for oligopeptides; probably responsible for the translocation of the substrate across the membrane
- Gene Name:
- oppC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AFH6
- Molecular weight:
- 33022
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a peptide intake transport system that plays a role in the resistance to antimicrobial peptides
- Gene Name:
- sapB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGH3
- Molecular weight:
- 36038
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Involved in a peptide intake transport system that plays a role in the resistance to antimicrobial peptides
- Gene Name:
- sapC
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AGH5
- Molecular weight:
- 31548
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Proton-dependent permease that transports di- and tripeptides. Has a clear preference for dipeptides and tripeptides composed of L-amino acids, and discriminates dipeptides on the basis of the position of charges within the substrate
- Gene Name:
- dtpB
- Uniprot ID:
- P36837
- Molecular weight:
- 53575
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable proton-dependent permease that transports di- and tripeptides. Shows significantly higher specificity towards dipeptides
- Gene Name:
- yjdL
- Uniprot ID:
- P39276
- Molecular weight:
- 53054
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Probable proton-dependent permease that transports dipeptides
- Gene Name:
- dtpD
- Uniprot ID:
- P75742
- Molecular weight:
- 54158
- General function:
- Involved in peptide transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Proton-dependent permease that transports di- and tripeptides as well as structurally related peptidomimetics such as aminocephalosporins into the cell. Has a clear preference for dipeptides and tripeptides composed of L-amino acids, and discriminates dipeptides on the basis of the position of charges within the substrate
- Gene Name:
- dtpA
- Uniprot ID:
- P77304
- Molecular weight:
- 53991
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppD
- Uniprot ID:
- P0AAG0
- Molecular weight:
- 35844
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Non-specific porin
- Gene Name:
- ompN
- Uniprot ID:
- P77747
- Molecular weight:
- 41220
- General function:
- Involved in nucleotide binding
- Specific function:
- Part of the binding-protein-dependent transport system for dipeptides. Probably responsible for energy coupling to the transport system
- Gene Name:
- dppF
- Uniprot ID:
- P37313
- Molecular weight:
- 37560
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Uptake of inorganic phosphate, phosphorylated compounds, and some other negatively charged solutes
- Gene Name:
- phoE
- Uniprot ID:
- P02932
- Molecular weight:
- 38922
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Dipeptide-binding protein of a transport system that can be subject to osmotic shock. DppA is also required for peptide chemotaxis
- Gene Name:
- dppA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23847
- Molecular weight:
- 60293
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- OmpF is a porin that forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane. It is also a receptor for the bacteriophage T2
- Gene Name:
- ompF
- Uniprot ID:
- P02931
- Molecular weight:
- 39333
- General function:
- Involved in transporter activity
- Specific function:
- Forms passive diffusion pores which allow small molecular weight hydrophilic materials across the outer membrane
- Gene Name:
- ompC
- Uniprot ID:
- P06996
- Molecular weight:
- 40368